A Simple but Critical Design Consideration
Draft is a simple design concept, and one every engineer—regardless of their chosen field—knows well. In pharmaceutical & biotechnology packaging, draft plays a critical role in ensuring a consistent end product that meets all mechanical, barrier, and efficiency requirements.
What is draft?
Draft (engineering): taper applied to surfaces or features perpendicular to the parting line of a molded part. It can be measured in degrees or mm/mm (in/in).1
When is it used?
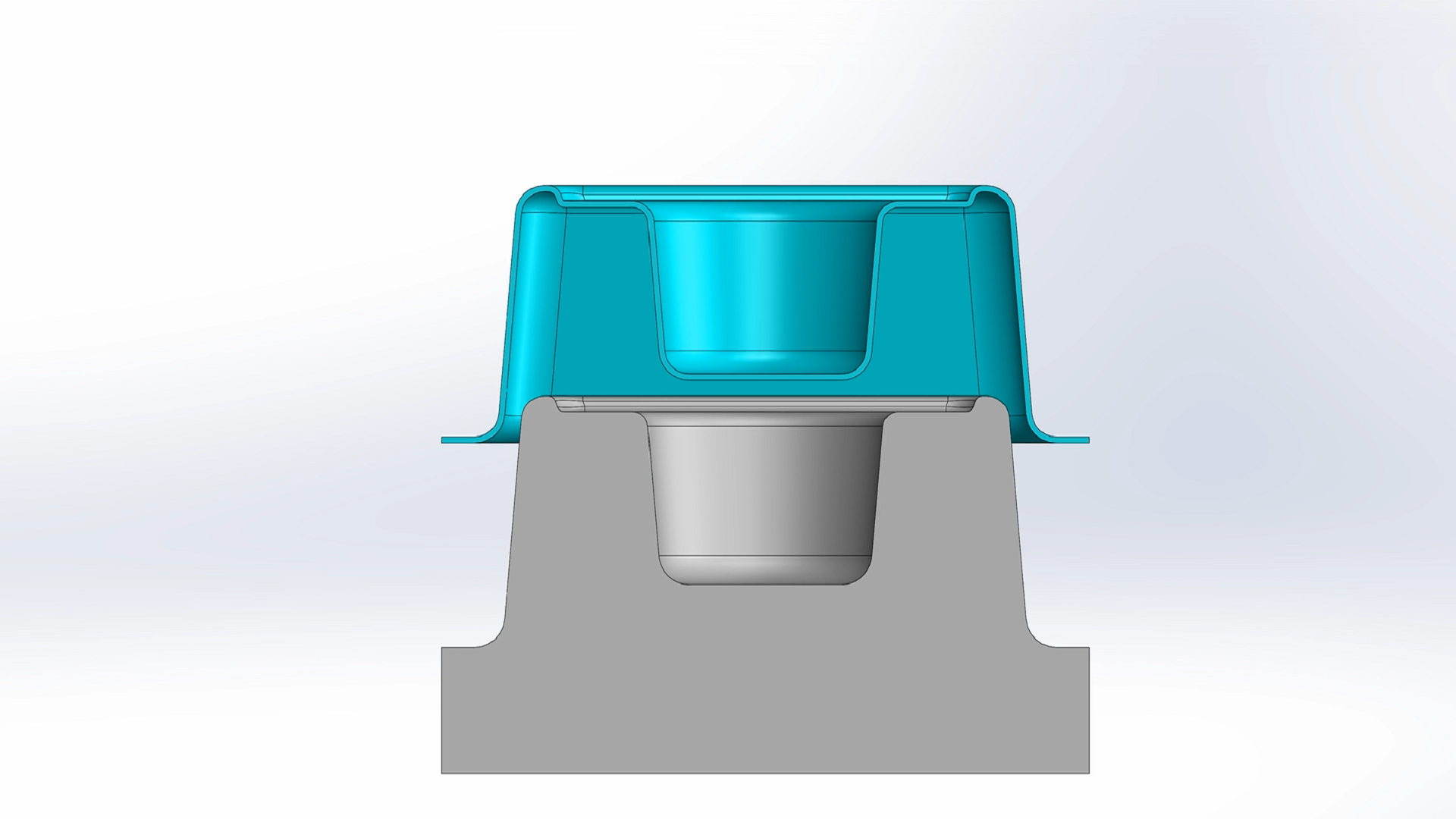
Draft is applied to cast, injection molded, cold formed, and thermoformed parts. In thermoforming, draft is essential to ensure depth of draw does not result in a compromised part. Too little or no draft will result in thin parts, poor barrier performance, compromised structural integrity, and parts which are difficult to remove from the mold.
How is draft used?
Draft is applied to the thermoform tool (mold) to help minimize thinning of the plastic as it is drawn over or into the mold. In this process, the heated plastic is formed under vacuum pressure against the surfaces of the mold. After the part is formed and the vacuum is released, the draft angle allows the part to be pulled off the mold. A properly designed mold will produce stronger parts with less material.
Pro Tip:
Did you know that well drafted parts can save your customer money? A part of the same thickness, if poorly drafted, will require more material to produce than one that is done correctly. Also, drafted parts stack! This will save your customer space in both inventory and shipping.
1 Definition referenced from Wikipedia, Draft (engineering).